Creating a 3D model from photos can be tough when the results look distorted or lack the detail you had in mind. Many designers and artists run into 3D models with inconsistent lighting, imperfect angles, or software that demands more precision than expected. The process can feel more technical than it should, especially when photo quality limits how accurate the final model becomes. This guide will help you create 3D model from photos and introduce a free AI tool that helps optimize source images for stronger results.

Step-by-Step Guide to Creating a 3D Model from Photos
Creating a solid 3Dmodel always begins with good photos. The best artists and 3D designers know that once the images are strong, being able to create 3D model from photos is much easier. Understanding the right capture technique eliminates 80% of the problems many of us can face later on in the process. Here’s how to photoshop convert image to 3D.
Phase 1: Capturing the Photos (The Most Important Step)
The first stage of creating a reliable 3D model begins with gathering a complete and consistent set of reference photos. Any gaps, harsh shadows, or shifts in lighting can introduce errors that show up later as warped surfaces or missing details.
Good images ensure the photogrammetry software has everything it needs to reconstruct the subject accurately. With the right preparation, even complex shapes become far easier to model. Using these tips can reduce the time spent on revising your models later on and help you create 3D model from photos.
Choose Your Subject: Select a non-reflective, textured object. Smooth or shiny surfaces lack distinguishable features, making it harder for photogrammetry software to track and align points accurately.
Lighting Matters: Diffused, even lighting produces the most reliable results. Cloudy outdoor conditions help eliminate harsh shadows, while indoor captures work best with soft, controlled light sources that minimize glare.
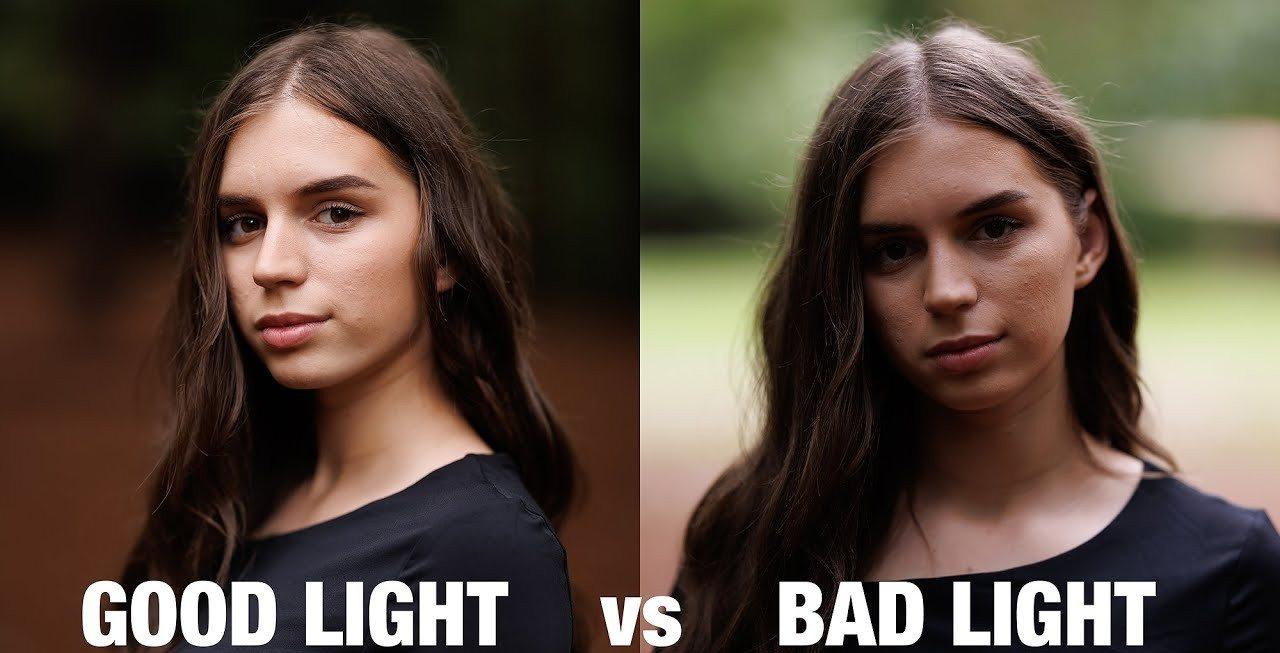

Capture Technique: Aim for 50–100+ photos, taken in a full circle around the subject. Maintain about 70–80% overlap between each shot, and include higher-angle images to ensure the software receives enough data to reconstruct top surfaces.
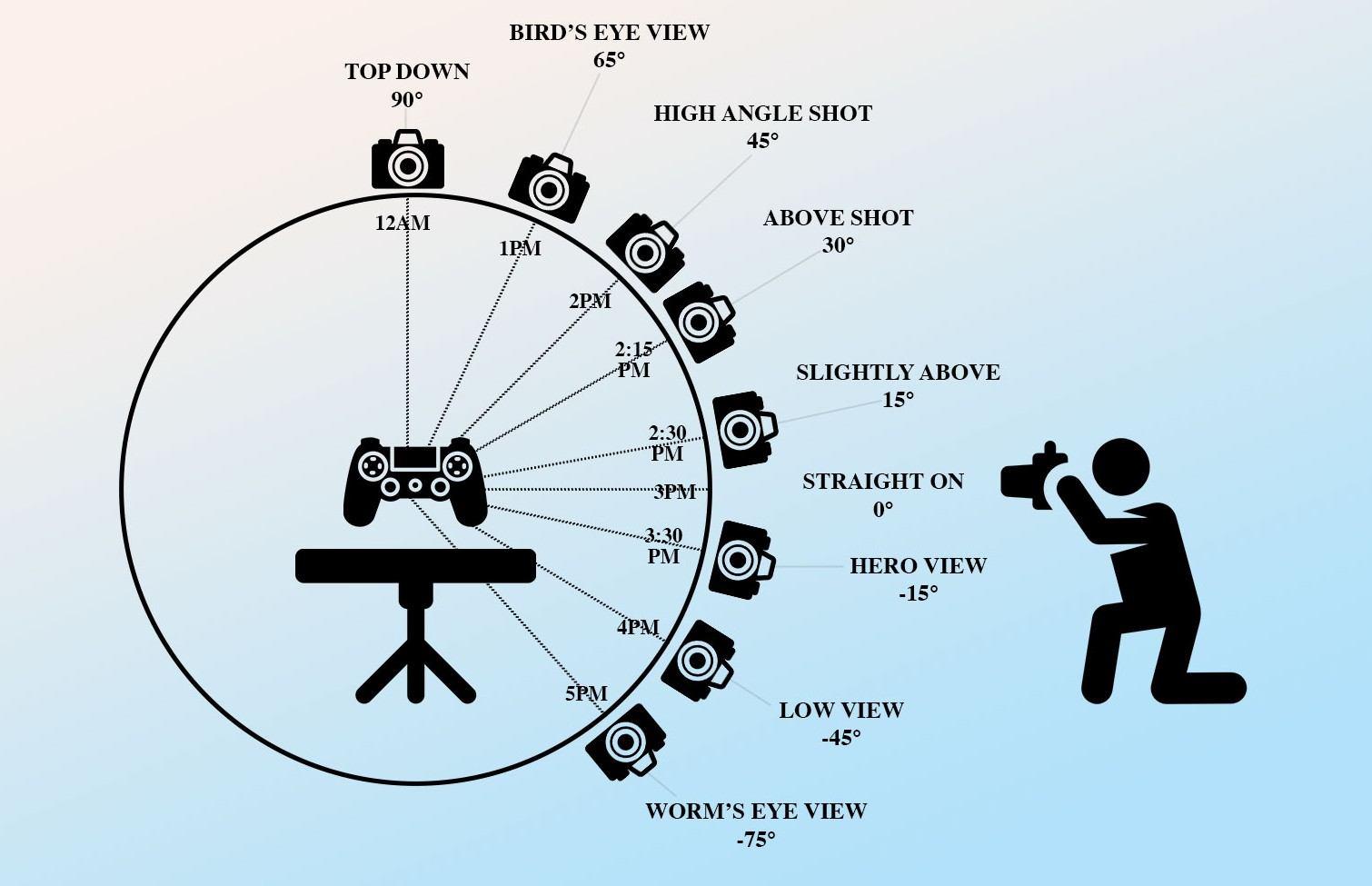
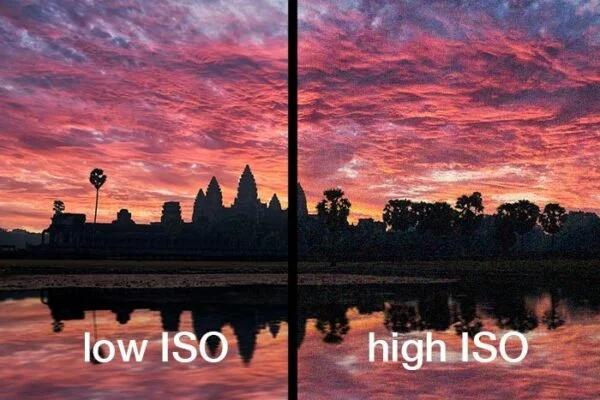
Camera Settings: A higher f-stop, such as f/8–f/11, keeps the entire subject sharp. Using a low ISO helps reduce noise. Many users rely on a smartphone in auto mode, which is perfectly acceptable as long as the lighting is strong and consistent.

Phase 2: Processing Photos into a 3D Model (Software Options)
With your photos ready, the next step is converting them into a usable 3D model. This phase handles alignment, point clouds, mesh building, and texturing. The right software makes a big difference in how clean and accurate the final result looks. Below are two reliable approaches creators use to turn image sets into detailed 3D models.
Method 1: Using Dedicated Photogrammetry Software (e.g., Meshroom, RealityCapture, Agisoft Metashape)
This method offers the most control over the final mesh and texture, making it ideal if you want professional results (e.g., Meshroom, RealityCapture). Here’s how to create a 3D model from photos using a free open-source software like Meshroom:
Step 1: Import all your captured images into the software. The software will automatically create a model for you.
Tip: Select only the images that are high quality.
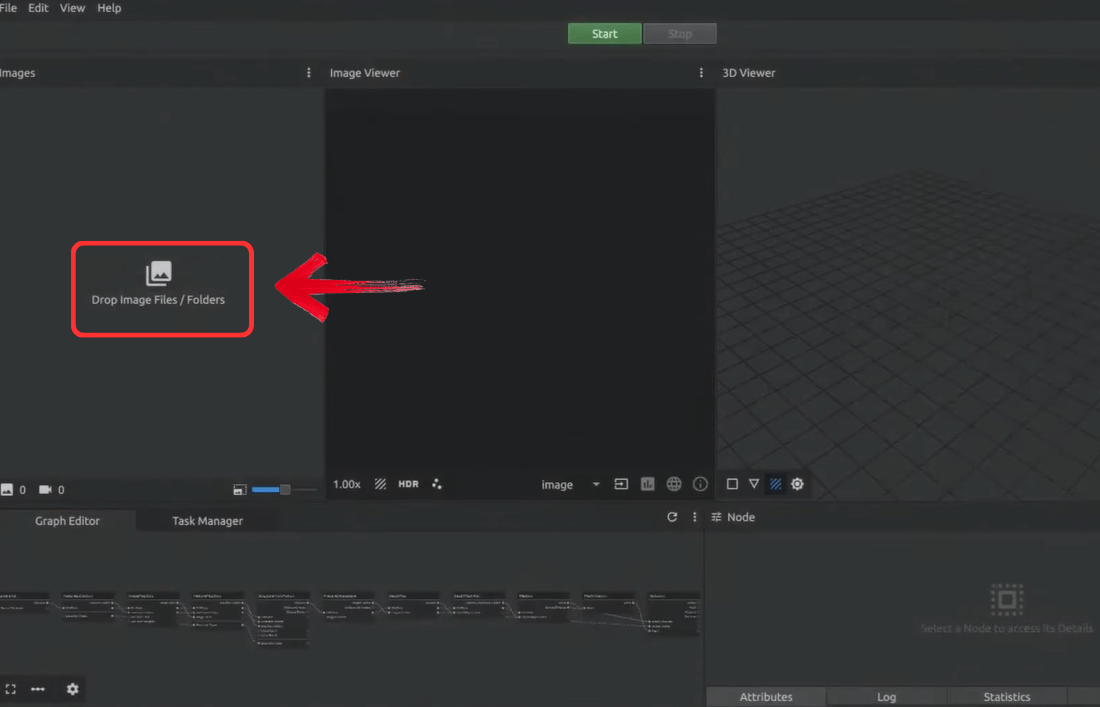
Step 2: The software automatically detects common points to calculate camera positions and create a sparse point cloud. You can use the cube tool to select which part of the image you want to keep.
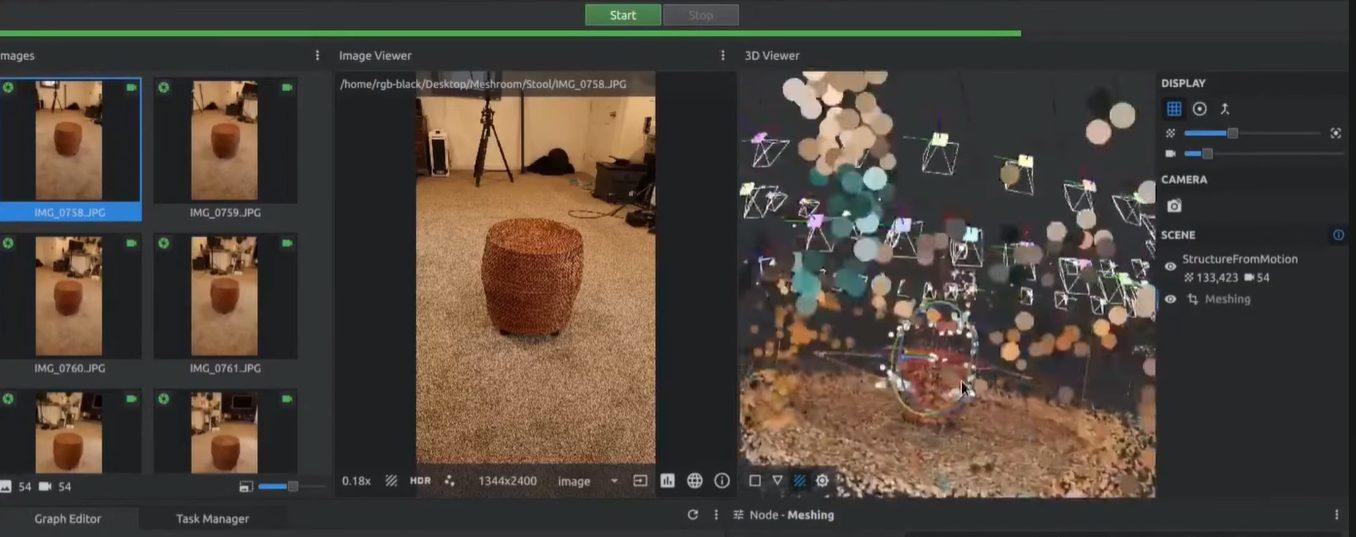
Step 3: The software generates a dense point cloud and then connects those points to create the 3D wireframe.
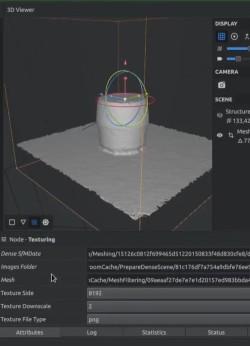
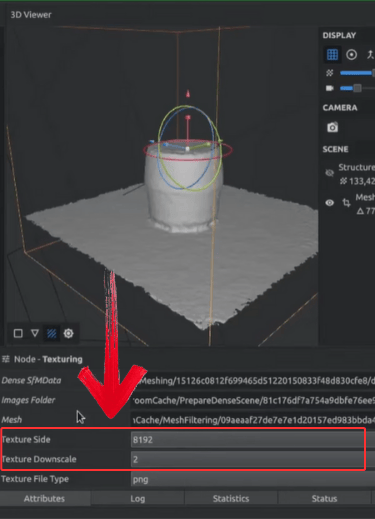
Step 4: Finally, add texture to the model by clicking "Texture Side" and "Texture Downscale". Play around with the settings and pick the one you find best for your model.
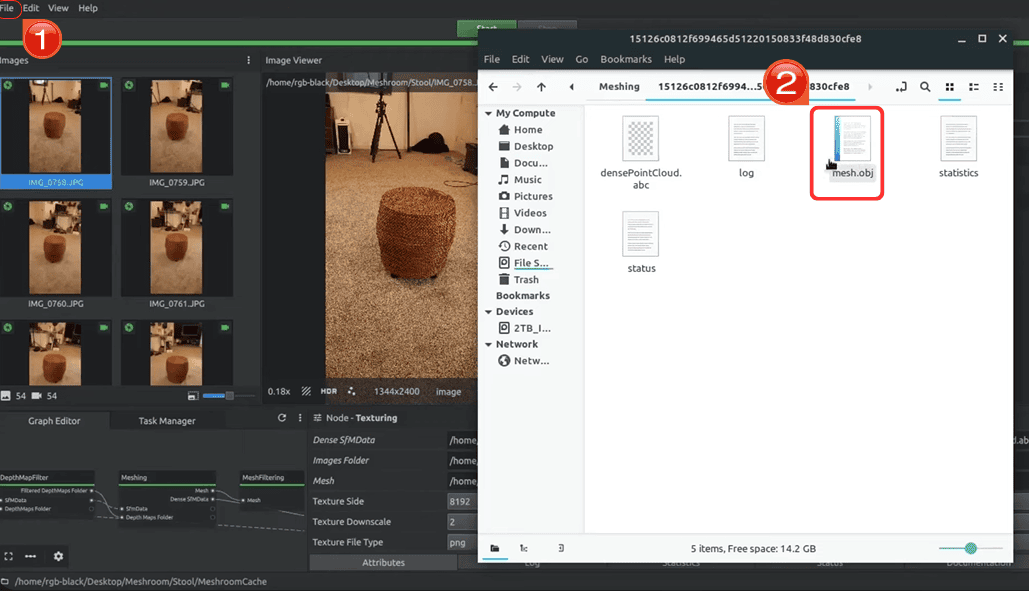
Step 5: Finally, select "File" in the top left and export the final model in a common format like.OBJ or .FBX.
Method 2: Using AI-Powered Online Tools (e.g., Hyper3D, Canva AI 3D Model Generator)
For speed and simplicity, these online options are fantastic, as they automate most of the complex alignment steps. Here’s how to create a 3D model from photos using Canva AI 3D model generator:
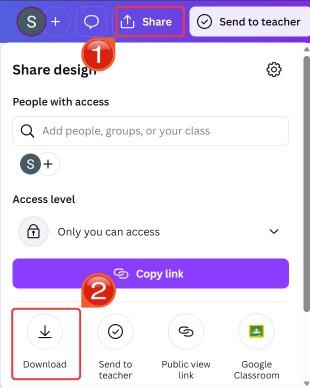
Step 1: Upload a set of photos of your object to the tool’s website.
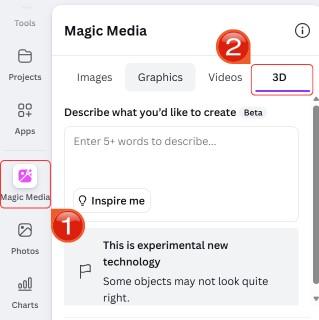
Step 2: Select “Magic Media” and then click on “3D” to start generating the 3D model from your image.
Step 3: Finally, click "Share" and then click "Download". These tools are often simpler but may offer less control than professional software.
Common Issues & How to Solve Them
Even with solid photos and the right tools, the first 3D result is not always perfect. Many people run into blurrytextures, missing geometry, or slow processing times. These issues are completely normal and usually trace back to lighting, coverage, or software alignment. With a few simple adjustments, most problems can be fixed quickly, and the overall model quality improves dramatically. Here are the most common challenges and practical ways to solve them.
Blurry or Noisy 3D Model
Cause: This usually happens when the input photos lack clarity. Motion blur, low light, or high ISO levels reduce the amount of detail the software can detect. Photogrammetry depends on sharp edges and texture patterns, so even small imperfections can degrade the model.
Solution: Use sharper, well-lit photos or enhance the ones you have. Image Enhancer can recover detail, reduce grain, and boost clarity so the software has better visual data to work with. If you prefer retaking the shots, stabilize the camera, increase lighting, or use a lower ISO to capture cleaner textures.
Holes or Incomplete Mesh
Cause: Missing geometry happens when certain surfaces weren’t photographed sufficiently. Highly reflective, transparent, or monochromatic areas also fail to register because the software struggles to identify unique points.
Solution: Take additional photos that cover the overlooked angles. If the object has smooth or glossy sections, place temporary markers like tape, sticky notes, or printed patterns to give the software something to track. Removing these markers in post-processing is far easier than repairing a broken mesh.
Model Looks Warped or Distorted
Cause: Misalignment during photo matching often causes bending or warping. This usually happens when images lack overlap or when different sides of the object have inconsistent lighting. The software relies on common visual features across multiple photos, so any inconsistency can break alignment.
Solution: Make sure each photo overlaps the previous one by at least 70 percent and avoid large jumps between angles. If the lighting varies, normalize brightness using Image Enhancer or other correction tools so the software sees consistent features across the set.
Processing Takes Too Long
Cause: Photogrammetry engines are computationally heavy. High-resolution photos or extremely large sets can overload your hardware and extend processing times.
Solution: Resize your photos to a moderate resolution before importing them. Images around 2 to 4 megapixels are usually enough for most objects. This reduces memory usage while keeping enough detail for a clean reconstruction. You can always reprocess at full resolution after validating the initial model.
Pro Tip: Time spent capturing photos properly saves far more time than trying to fix a broken mesh later.
Enhance Your Source Photos with Image Enhancer
Even the best photos can have small issues like slight blur, noise, or low resolution, which can make 3D models less sharp and detailed. Retaking tons of photos can be exhausting and time-consuming. You could, however, instead of retaking every image again, put them through an image enhancer tool and upscale the image to remove any blurs and turn them into high-definition wonders.
Toolsmart Image Enhancer is a free AItool that fixes these problems by sharpening, denoising, and upscaling images quickly. Using it before creating your 3D model ensures cleaner, more accurate results with realistic textures. Its simple interface makes it easy to enhance multiple photos at once, saving time when working with large projects.
Key Features for Image Optimization:
Free & Instant: No sign-up required for basic enhancement.
AI-Powered Upscale: Increases image size without losing quality, providing more data for 3D reconstruction.
Sharpness & Noise Reduction: Automatically improves clarity, sharpens details, and minimizes noise.
Batch Processing: Enhance multiple photos at once, perfect for preparing a full set for 3D modeling.
How to Use Image Enhancer Before 3D Modeling
Using Toolsmart’s Image Enhancer is incredibly straightforward, even if you’re not a tech expert. I always appreciate tools that get straight to the point without unnecessary complications, and this one fits the bill perfectly. Here’s how you can quickly enhanceyour images in just a few simple steps:
Step 1: Head on over to the Toolsmart Free Image Enhancer website.

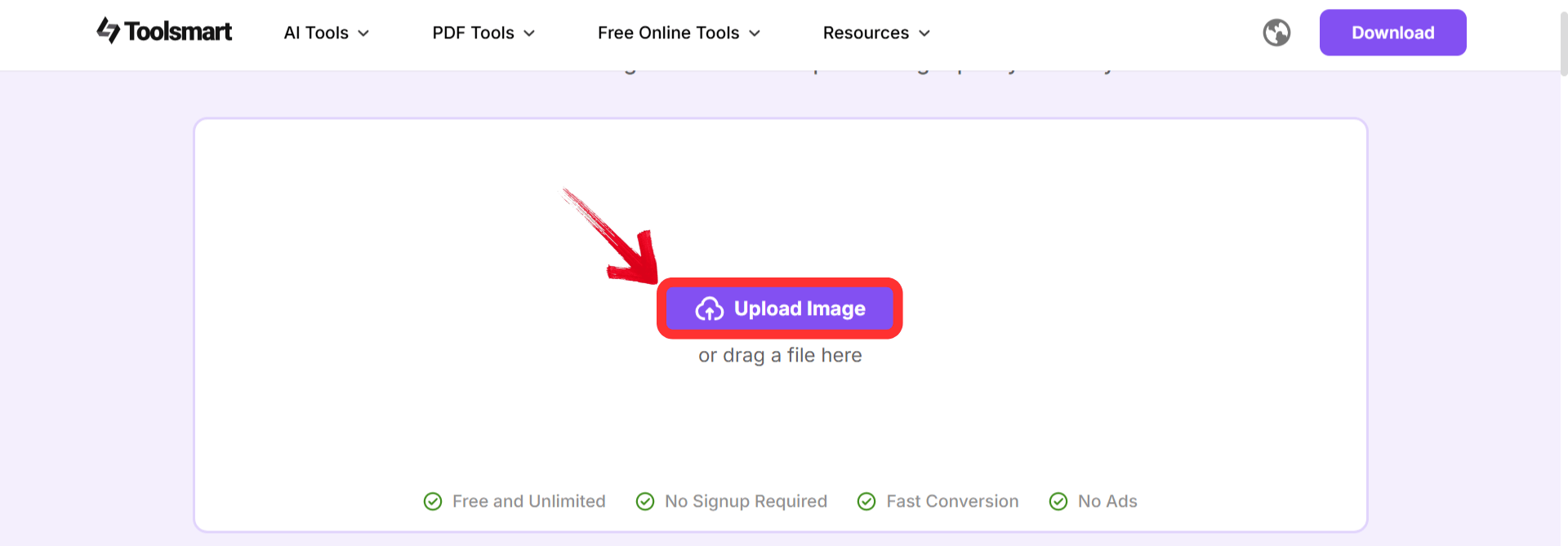
Step 2: Click on the “Upload image”option or drag your image directly onto the screen
Step 3: Once you’re done, click“Download” to save it to your device.
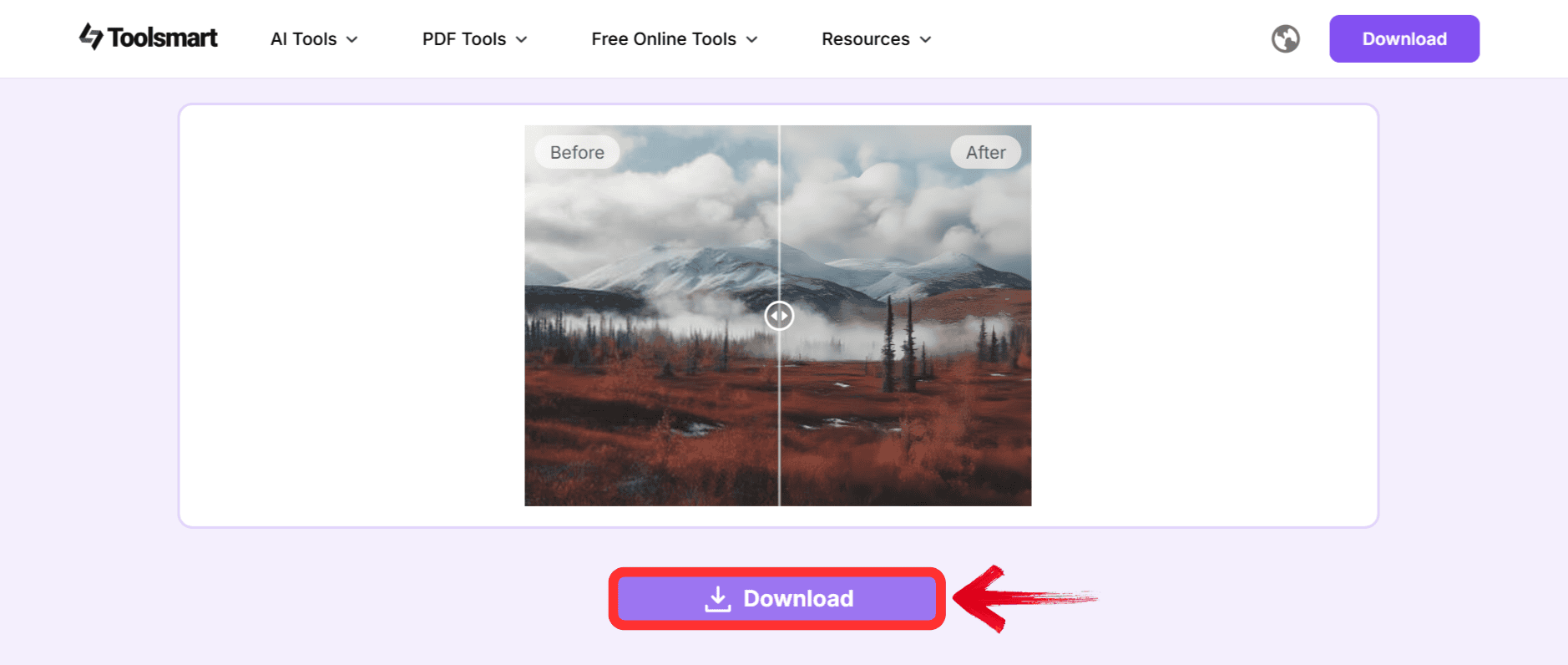
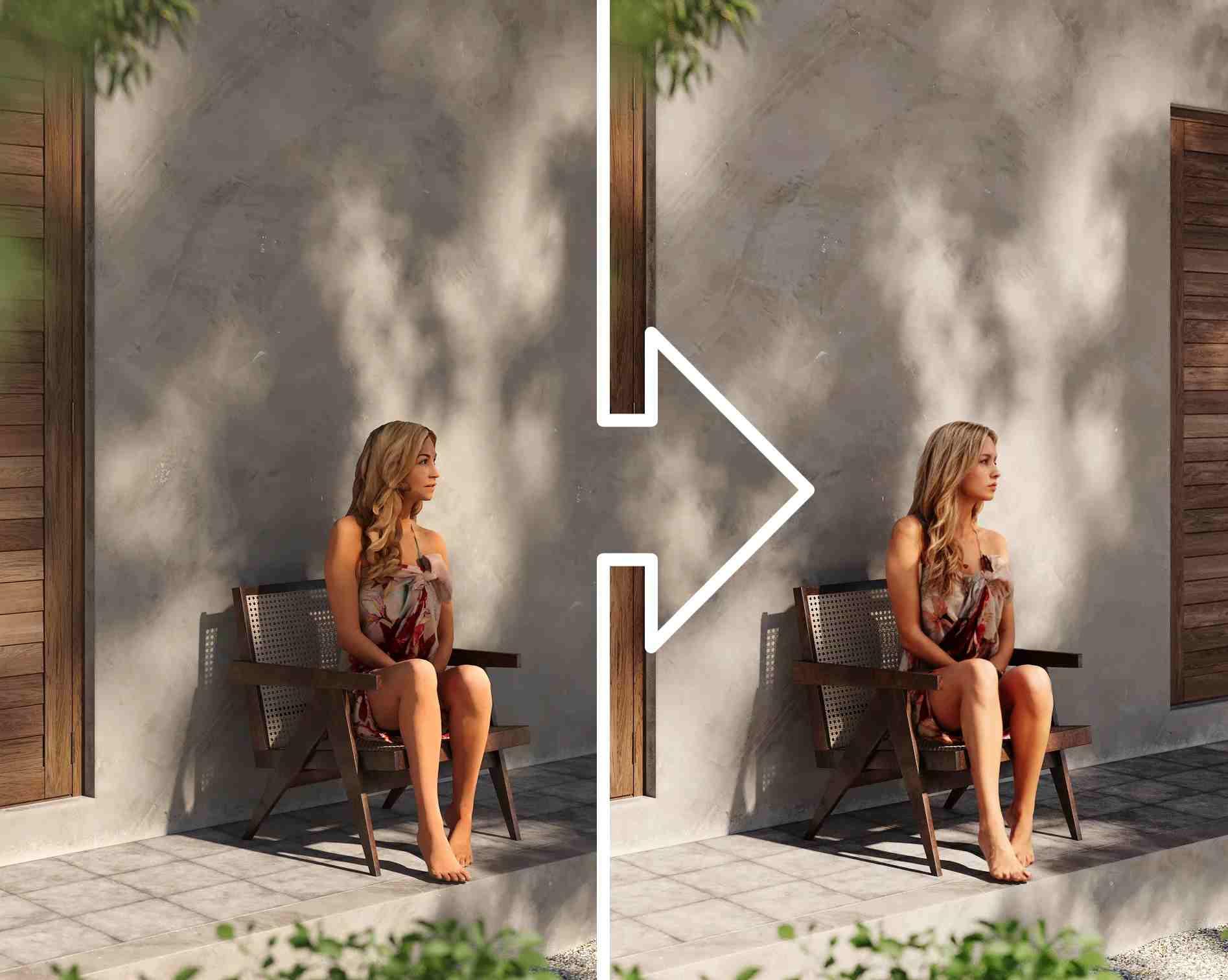
It’s that simple. I appreciate how streamlined the whole process is; no complicated menus or hidden fees, just clean, high-quality results fast. Below, you can see what difference the Toolsmart AI image Enhancer can make to the quality of your 3D model.
FAQs
Q1: How many photos do I need to create a 3D model?
It depends on the object’s complexity, but typically 50–100 well-captured photos from all angles are a good starting point.
Q2: Can I use my smartphone to take the photos?
Yes, modern smartphones have excellent cameras suitable for photogrammetry. Just ensure good lighting and stability.
Q3: What’s the difference between photogrammetry software and AI generators?
Photogrammetry software (like Meshroom) offers more control and potentially higher quality but has a steeper learning curve. AI generators (like Hyper3D) are faster and easier but may be less detailed.
Q4: Is Image Enhancer really free?
Yes, the core enhancement features are free to use without watermarks.
Q5: Can I create a 3D model from a single photo?
While some advanced AI tools are emerging for single-image 3D reconstruction, results are often less accurate than multi-image photogrammetry. Using multiple photos is strongly recommended for quality models.
My Final Thoughts
Mastering the process to create 3D model from photosis far more accessible now than ever before. High-quality, overlapping input photos are the most important step to generating consistent high-quality 3D models. By understanding the fundamentals of photogrammetry and leveraging free tools like Toolsmart AI Image Enhancer to optimize your source images, you can achieve professional-grade results. This combination of smart capture and AI processing is the key to successfully transforming 2D images into detailed 3D assets.

